 Esperanto
Esperanto
 Shqiptare
Shqiptare
 Euskara
Euskara
 Zulu
Zulu
 Latinus
Latinus
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
 Slovak
Slovak
 Slovak
Slovak
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
News Center
What is Current Transformer ?
Publish:
2022-09-14 22:55
Source:
www.premier-cable.net
Current Transformer
A current transformer is an instrument that converts a large current on the primary side into a small current on the secondary side for measurement based on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
A current transformer consists of a closed iron core and windings. Its primary side winding has few turns, and it is connected in the line of the current that needs to be measured.
Therefore, it often has all the current of the line flowing through it, and the secondary winding has a large number of turns. It is connected in series in the measuring instrument and the protection circuit.
When the current transformer is working, its secondary circuit is always closed, so the measurement The impedance of the series coil of the instrument and the protection circuit is very small, and the working state of the current transformer is close to a short circuit.
The current transformer is to convert the large current on the primary side into a small current on the secondary side for measurement, and the secondary side cannot be opened.
Introduction
The principle of current transformer is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
A current transformer consists of a closed iron core and windings.
Its primary winding has a small number of turns, and it is connected in the line of the current that needs to be measured, so it often has all the current of the line flowing through it, and the secondary winding has a large number of turns.
When the transformer is working, its secondary circuit is always closed, so the impedance of the series coil of the measuring instrument and the protection circuit is very small, and the working state of the current transformer is close to a short circuit.
Working principle
In the lines of power generation, substation, transmission, distribution and consumption, the current varies greatly, ranging from a few amperes to tens of thousands of amperes.
In order to facilitate measurement, protection and control, it needs to be converted into a relatively uniform current.
In addition, the voltage on the line is generally relatively high, such as direct measurement, which is very dangerous.
The current transformer plays the role of current transformation and electrical isolation
For pointer-type ammeters, most of the secondary currents of the current transformers are in the ampere level (such as 5A, etc.).
For digital instruments, the sampled signal is generally at the milliamp level (0-5V, 4-20mA, etc.).
The secondary current of the miniature current transformer is milliampere, which mainly acts as a bridge between the large transformer and the sampling.
Similar to the transformer, the current transformer also works according to the principle of electromagnetic induction.
The transformer transforms the voltage and the current transformer transforms the current.
The winding of the current transformer connected to the measured current (the number of turns is N1) is called the primary winding (or the primary winding, the primary winding); the winding connected to the measuring instrument (the number of turns is N2) is called the secondary winding (or secondary winding). winding, secondary winding).
The current ratio of the primary winding current I1 to the secondary winding I2 of the current transformer is called the actual current ratio K.
The current ratio of the current transformer when it works under the rated current is called the rated current ratio of the current transformer, expressed by Kn.
Kn=I1n/I2n
Current transformer, referred to as CT for short, is used to convert a primary current with a larger value into a secondary current with a smaller value through a certain transformation ratio, which is used for protection, measurement and other purposes. For example, a current transformer with a ratio of 400/5 can convert an actual current of 400A into a current of 5A.
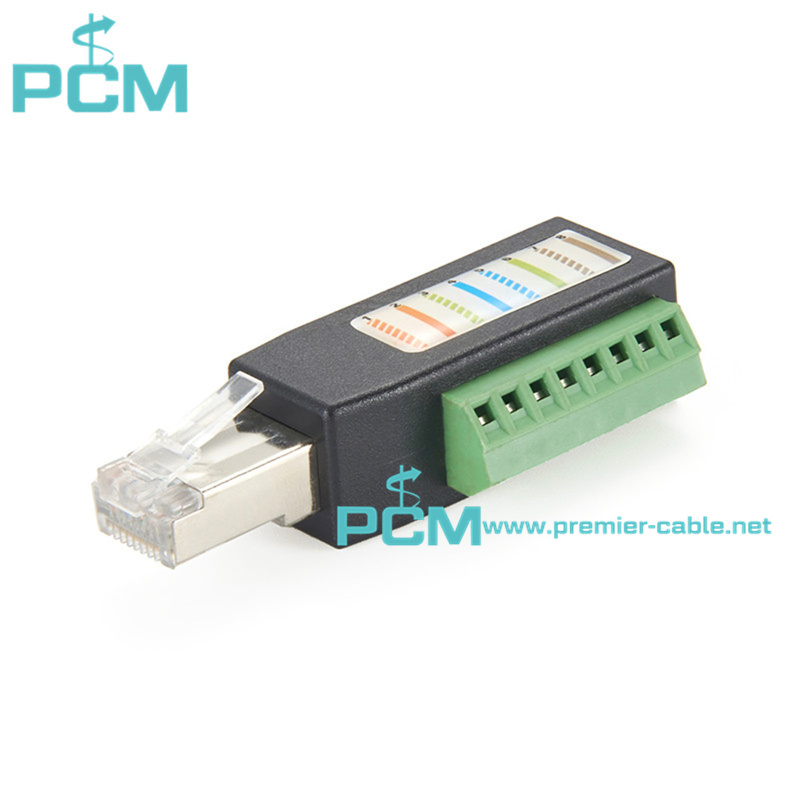
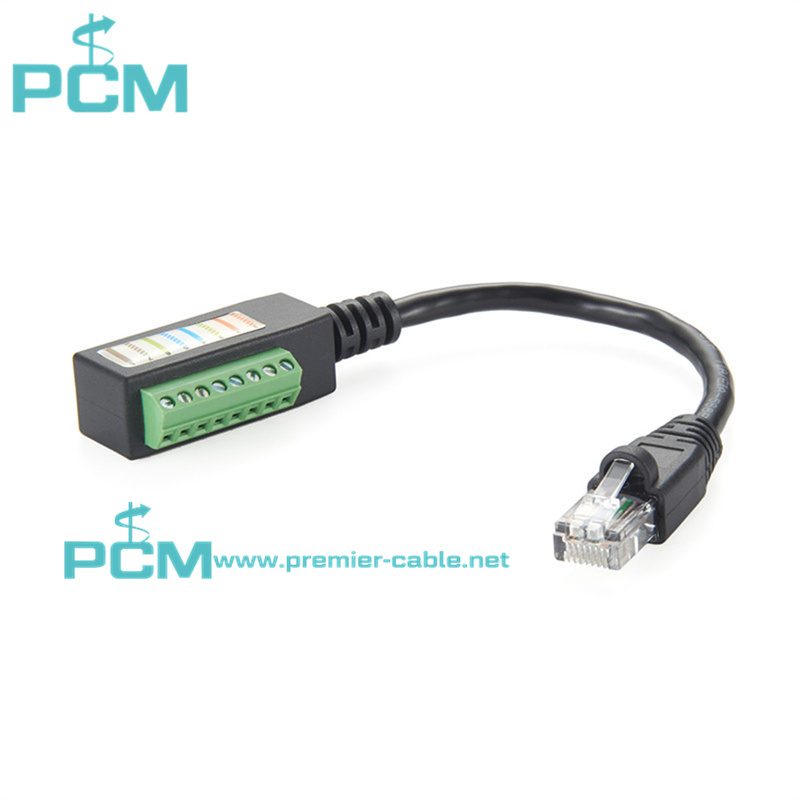
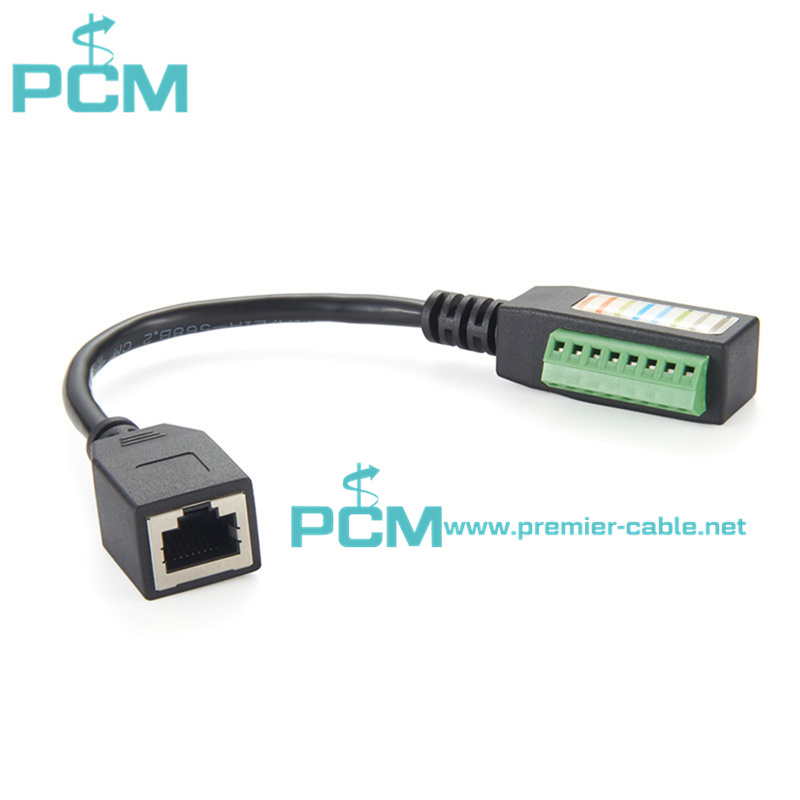
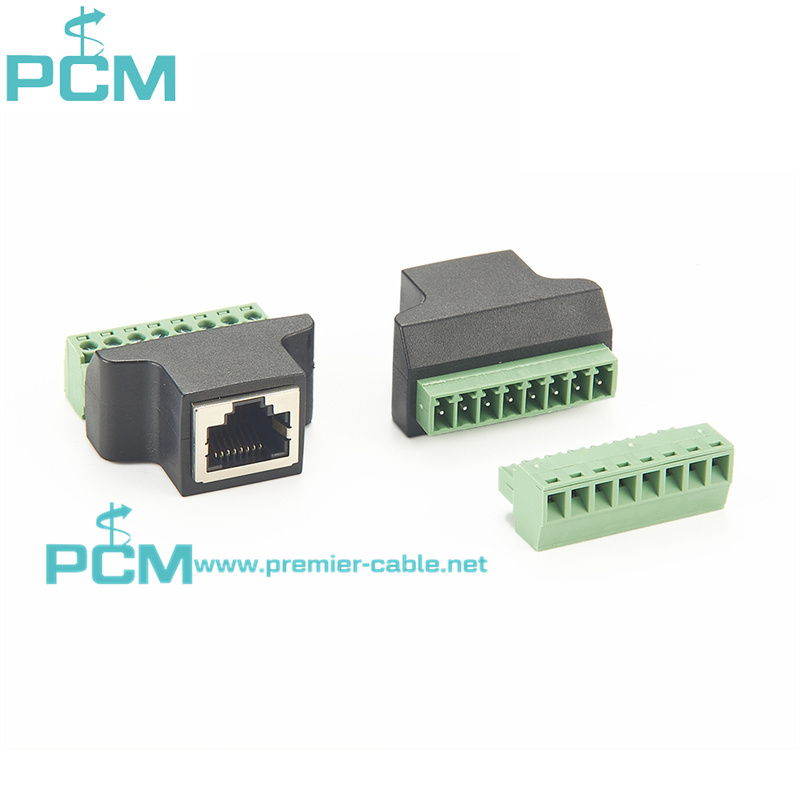
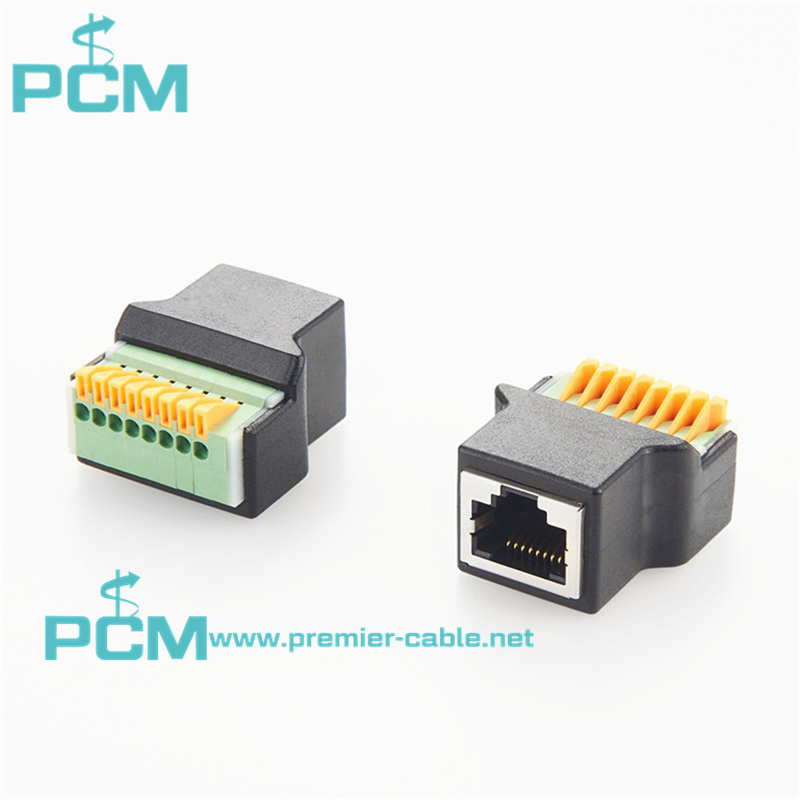
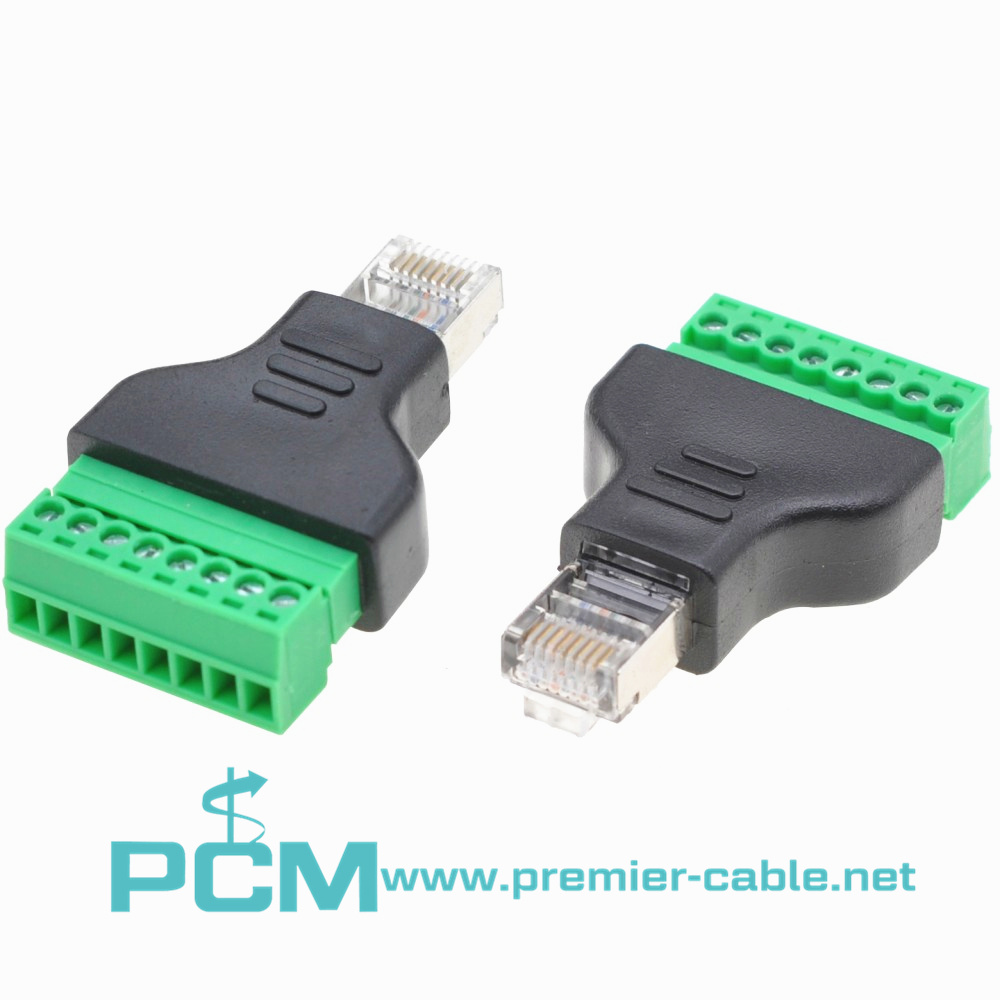
Current Transformer Kit RJ45
Power Measuring System 8 pin RJ45 connector
Accessories for low-voltage current transformer
Split-core current transformer RJ45 Plug adaptor
Adapter Connector RJ45 Male Terminal Block 8 pin
RJ45 Plug adaptor for measuring split-core current transformer




Related News
What is a terminal block used for?
While there are many factors to consider when designing an overall system, terminal blocks are an optimal solution for complex electrical system connections. With a variety of color options and configurations, Premier Cable’ terminal blocks offer a range of options to meet your design challenges.
CAN-bus has been widely used in various automation control systems. For example, CAN-bus has incomparable advantages in various fields such as automotive electronics, automatic control, smart buildings, power systems, and security monitoring.
Introduction to M12 connector pin coding
M12 encoding types are A encoding, B encoding, D encoding and X encoding. A-code, B-code and X-code are some of the earliest developed and longest-available M12 connectors. The latest M12 coding types currently under development are K coding for AC and L coding for PROFINET DC.
Cables – What are the correct cable sizes for an NMEA 2000 network?
The three different sizes of NMEA 2000 certified DeviceNet standard cabling are "micro," "mid," and "mini."
What are the advantages of NMEA 2000?
The Premier Cable Starter Kits provide everything you need to get to create a basic NMEA 2000 network from scratch.
The role of DeviceNet terminal resistor
DeviceNet_network is a fieldbus network protocol based on Controller Area Network (CAN). In the DeviceNet network, the terminal resistor plays the role of compensation and protection for signal transmission. The function of the terminal resistor is to eliminate signal reflection and interference and ensure the signal transmission quality.
